Generative models for the request for quote activity¶
Simulation of RfQs arrival and client attrition¶
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import poisson, norm
from collections import deque
def run_simulation(N_clients=50,
T=200,
reservation_price_mean=100,
reservation_price_std_pct=0.1,
lambda_mean=1,
lambda_std=0.05,
prior_mean=60,
prior_std=10,
res_price_noise_std_pct=0.2,
hit_rate_target=0.4,
window_size=10,
attrition_threshold=0.1):
"""
Simulate RFQ interactions with Bayesian quantile pricing and client attrition.
Clients stop trading if their moving-average hit rate over `window_size` days falls below `attrition_threshold`.
Returns:
rfq_df: DataFrame of RfQ events
active_history: list of active client counts per day
activity_matrix: binary DataFrame of daily activity (clients x days)
"""
np.random.seed(42)
# Generate distribution of reservation prices for the segment of clients
reservation_prices = np.random.normal(reservation_price_mean,
reservation_price_mean * reservation_price_std_pct,
N_clients)
# Reservation prices are noisy given potential changing market conditions
res_price_noise_std = res_price_noise_std_pct * reservation_price_mean
res_price_noise_var = res_price_noise_std**2
# Generate distribution of RfQ intensities for the segment of clients
lambdas = np.abs(np.random.normal(lambda_mean, lambda_std, N_clients))
clients_posterior = {i: {'mean': prior_mean, 'var': prior_std**2,
'n': 0, 'sum_obs': 0.0}
for i in range(N_clients)}
z = norm.ppf(1 - hit_rate_target)
active = np.ones(N_clients, dtype=bool)
# Track per-client active status at end of each day
active_flags = np.zeros((T, N_clients), dtype=bool)
daily_history = [deque(maxlen=window_size) for _ in range(N_clients)]
active_history = []
records = []
Y = np.zeros((T, N_clients), dtype=int)
for t in range(T):
daily_hits = np.zeros(N_clients, dtype=int)
daily_reqs = np.zeros(N_clients, dtype=int)
for i in range(N_clients):
if not active[i]: continue
n_rfq = poisson.rvs(lambdas[i])
if n_rfq > 0: Y[t,i] = 1
for _ in range(n_rfq):
post = clients_posterior[i]
price = max(0.0, post['mean'] + np.sqrt(post['var'] + res_price_noise_var) * z)
r = norm.rvs(reservation_prices[i], res_price_noise_std)
# Trading happens when price offered is lower than the reservation price
hit = price <= r
daily_reqs[i] += 1; daily_hits[i] += int(hit)
# The dealer updates the estimation of the reservation price of the client
post['n'] += 1; post['sum_obs'] += r
post_var = 1/(1/prior_std**2 + post['n']/res_price_noise_var)
post['var'] = post_var
post['mean'] = post_var*(prior_mean/prior_std**2 + post['sum_obs']/res_price_noise_var)
records.append({'time': t, 'client_id': i, 'price': price, 'hit': hit})
for i in range(N_clients):
if not active[i] or daily_reqs[i]==0: continue
rate = daily_hits[i]/daily_reqs[i]
daily_history[i].append(rate)
# A client stops sending RfQs to the dealer if the hit & miss is too low
if len(daily_history[i])==window_size and np.mean(daily_history[i])<attrition_threshold:
active[i] = False
active_history.append(active.sum())
active_flags[t, :] = active.copy()
rfq_df = pd.DataFrame(records)
activity = pd.DataFrame(Y, columns=[f'client_{i}' for i in range(N_clients)])
active_df = pd.DataFrame(active_flags, columns=[f'client_{i}' for i in range(N_clients)])
return rfq_df, active_history, activity, active_df
from scipy.special import betaln
from scipy.optimize import minimize
# ----------------------
# Segment-level Model
# ----------------------
def estimate_segment_params(activity_matrix):
def log_marginal_likelihood(D, alpha, beta, gamma, delta):
n, x = len(D), D.sum()
last = np.where(D==1)[0]
r = n - (last[-1]+1) if last.size>0 else n
logA = (betaln(alpha+x, beta+n-x)-betaln(alpha,beta)
+betaln(gamma, delta+n)-betaln(gamma,delta))
logB = [(betaln(alpha+x, beta+n-x-i)-betaln(alpha,beta)
+betaln(gamma+1, delta+n-i)-betaln(gamma,delta))
for i in range(1, r+1)]
mags = [logA] + logB; m_max = max(mags)
return m_max + np.log(sum(np.exp(m - m_max) for m in mags))
def neg_ll(params):
alpha, beta, gamma, delta = np.exp(params)
return -sum(log_marginal_likelihood(activity_matrix.iloc[:end, j].values,
alpha, beta, gamma, delta)
for j in range(activity_matrix.shape[1])
for end in [activity_matrix.iloc[:,:].values.shape[0]])
res = minimize(neg_ll, np.log([1,1,1,1]), method='L-BFGS-B', bounds=[(-5,5)]*4)
return np.exp(res.x)
def attrition_probability(D, alpha, beta, gamma, delta):
n, x = len(D), D.sum()
last = np.where(D==1)[0]
r = n - (last[-1]+1) if last.size>0 else n
logA = (betaln(alpha+x, beta+n-x)-betaln(alpha,beta)
+betaln(gamma, delta+n)-betaln(gamma,delta))
logB = [(betaln(alpha+x, beta+n-x-i)-betaln(alpha,beta)
+betaln(gamma+1, delta+n-i)-betaln(gamma,delta))
for i in range(1, r+1)]
mags = [logA] + logB; m_max = max(mags)
logL = m_max + np.log(sum(np.exp(m - m_max) for m in mags))
P_active = np.exp(logA - logL)
return 1 - P_active
from sklearn.metrics import (
confusion_matrix, accuracy_score,
precision_score, recall_score,
roc_curve, auc
)
# ----------------------
# Workflow: Simulate, Train, Test
# ----------------------
T_train, T_test = 100, 100
T_tot = T_train + T_test
N_clients = 50
rfq_all, active_all, Y_all, active_df = run_simulation(N_clients = N_clients, T=T_train+T_test)
Y_train = Y_all.iloc[:T_train].reset_index(drop=True)
Y_test = Y_all.iloc[T_train:].reset_index(drop=True)
rfq_test = rfq_all[rfq_all['time']>=T_train].copy()
rfq_test['time'] -= T_train
active_test = active_all[T_train:]
alpha, beta, gamma, delta = estimate_segment_params(Y_train)
print(f"Params: α={alpha:.2f}, β={beta:.2f}, γ={gamma:.2f}, δ={delta:.2f}")
# ----------------------
# Risk Scoring
# ----------------------
risk_records = []
for j in range(Y_test.shape[1]):
hist = []
for t in range(T_test):
hist.append(Y_test.iloc[t, j])
D = np.array(hist, dtype=int)
p_inact = attrition_probability(D, alpha, beta, gamma, delta)
risk_records.append({
'time': t,
'client_id': j,
'p_inactive': p_inact,
'alert': p_inact > 0.5 # thresholded prediction
})
risk_df = pd.DataFrame(risk_records)
# Label inactivity
risk_df['inactive'] = risk_df.apply(
lambda r: not active_df.loc[r['time'] + T_train, f'client_{r["client_id"]}'],
axis=1
)
# ----------------------
# Evaluation Metrics
# ----------------------
# Ground truth and predictions
y_true = risk_df['inactive']
y_pred = risk_df['alert'] # at 0.5 threshold
y_scores = risk_df['p_inactive'] # raw probabilities
# Confusion matrix
tn, fp, fn, tp = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred).ravel()
print("Confusion Matrix:")
print(f" TN={tn}, FP={fp}, FN={fn}, TP={tp}")
# Accuracy, Precision, Recall at 0.5
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred)
precision = precision_score(y_true, y_pred)
recall = recall_score(y_true, y_pred)
print(f"Accuracy : {accuracy:.4f}")
print(f"Precision: {precision:.4f}")
print(f"Recall : {recall:.4f}")
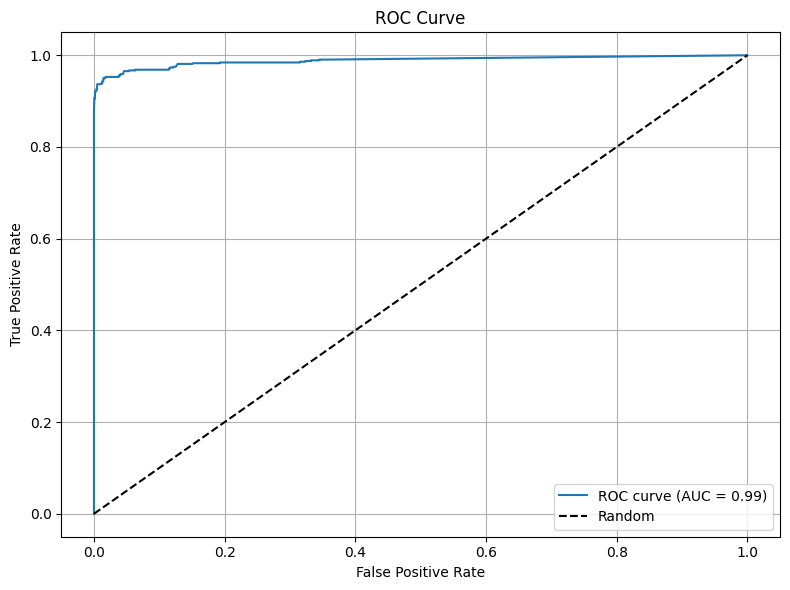
# ROC curve & AUC
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_true, y_scores)
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
print(f"AUC : {roc_auc:.4f}")
# Plot ROC
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, label=f'ROC curve (AUC = {roc_auc:.2f})')
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], 'k--', label='Random')
plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate')
plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate')
plt.title('ROC Curve')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Params: α=148.41, β=85.31, γ=0.08, δ=148.41
Confusion Matrix:
TN=4365, FP=0, FN=76, TP=559
Accuracy : 0.9848
Precision: 1.0000
Recall : 0.8803
AUC : 0.9884
# ----------------------
# Plots: Hit Rate & Attrition Over Full Simulation
# ----------------------
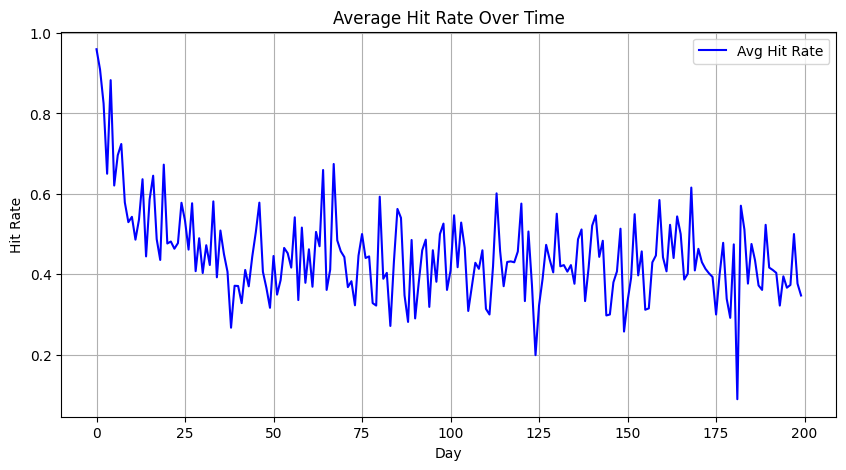
# Active-client hit rate over time
hit_rate_active = []
days = np.arange(T_tot)
for t in days:
act_clients = active_df.iloc[t]
active_ids = [int(col.split('_')[1]) for col, flag in act_clients.items() if flag]
daily = rfq_all[rfq_all['time'] == t]
rates = []
for cid in active_ids:
cr = daily[daily['client_id'] == cid]
if not cr.empty:
rates.append(cr['hit'].mean())
hit_rate_active.append(np.mean(rates) if rates else np.nan)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.plot(days, hit_rate_active, label='Avg Hit Rate', color='blue')
plt.title('Average Hit Rate Over Time')
plt.xlabel('Day'); plt.ylabel('Hit Rate'); plt.grid(True); plt.legend()
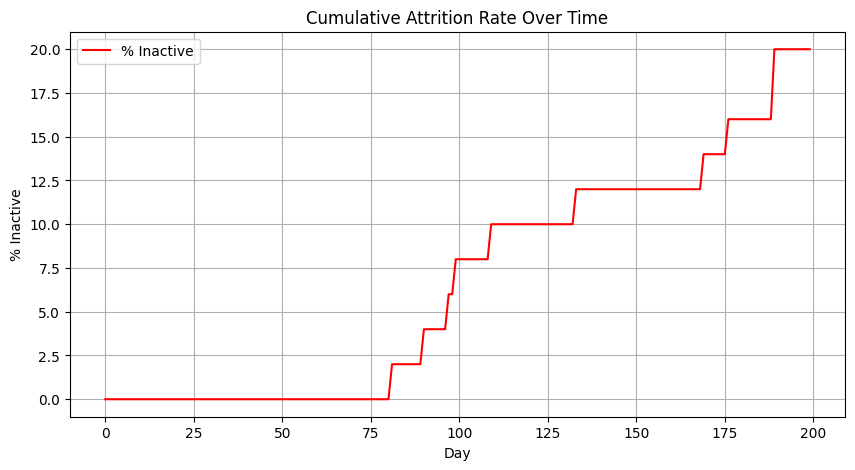
# Attrition rate over time
attr_rate = [100 * (Y_all.shape[1] - x) / Y_all.shape[1] for x in active_all]
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.plot(days, attr_rate, label='% Inactive', color='red')
plt.title('Cumulative Attrition Rate Over Time')
plt.xlabel('Day'); plt.ylabel('% Inactive'); plt.grid(True); plt.legend()
# ----------------------
# Model Fit Visualization
# ----------------------
# Compare predicted attrition vs actual on test
pred_rate = risk_df.groupby('time')['p_inactive'].mean()
actual_rate = [100*(N_clients-x)/N_clients for x in active_test]
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.plot(pred_rate.index, 100*pred_rate.values, label='Predicted % Inactive')
plt.plot(actual_rate, label='Actual % Inactive')
plt.title('Predicted vs Actual Attrition (Test Set)')
plt.xlabel('Day'); plt.ylabel('% Inactive'); plt.legend(); plt.grid(True)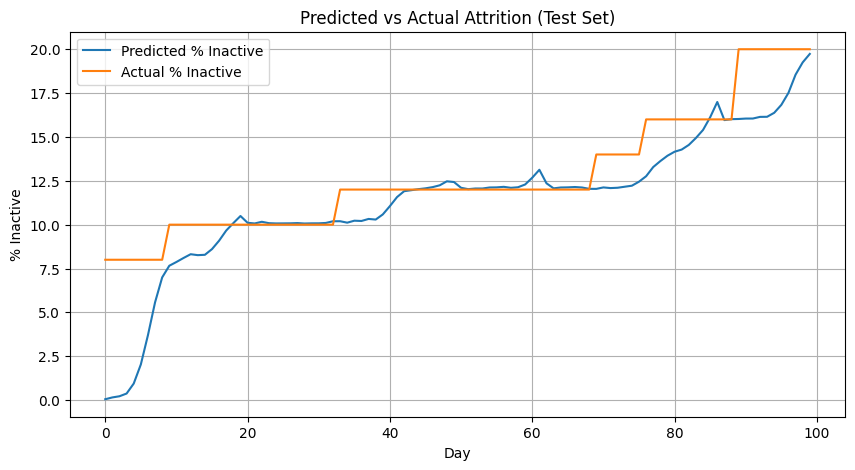
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# ----------------------
# Function: Plot Clients by ID (single figure with subplots)
# ----------------------
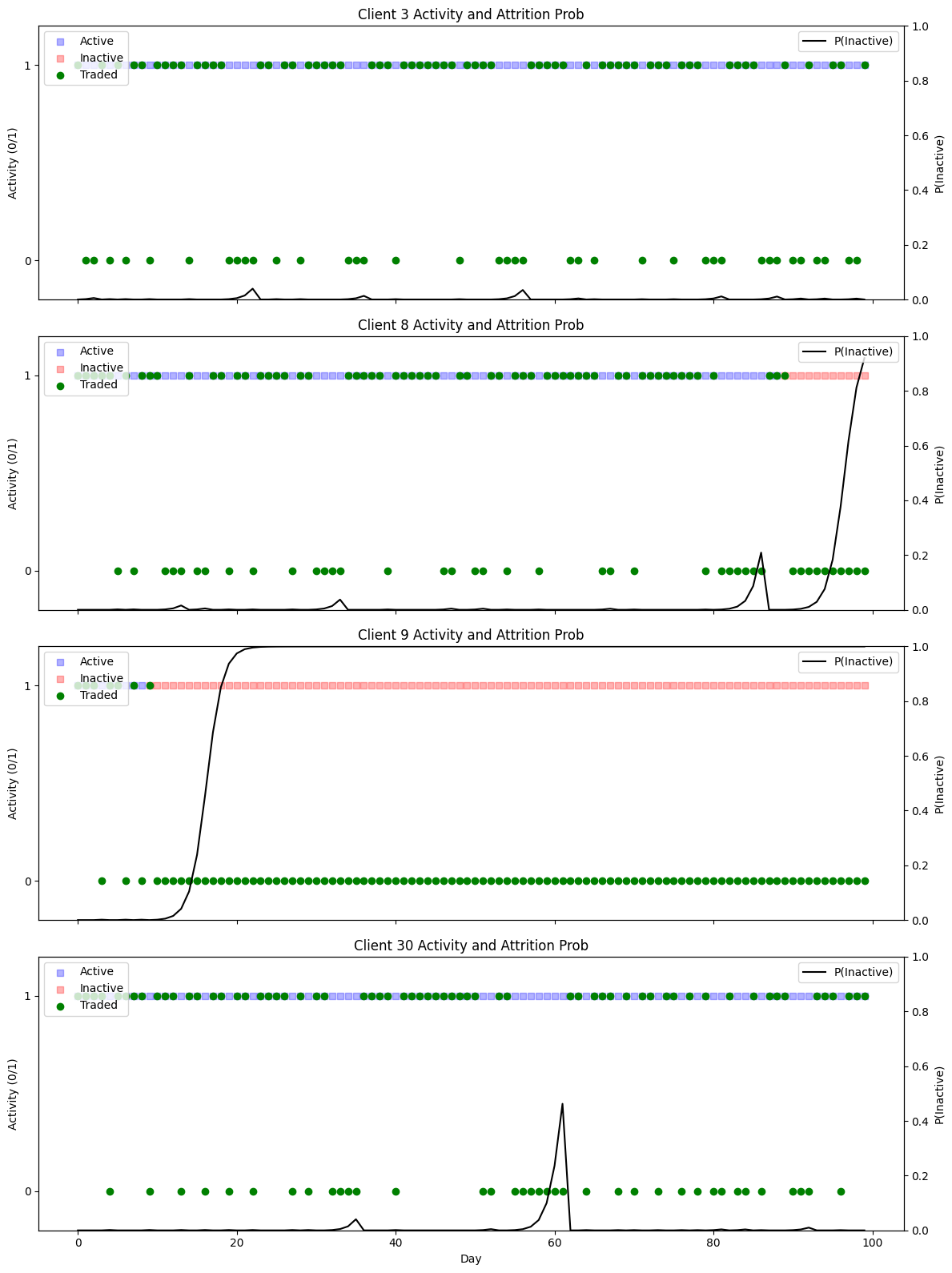
def plot_clients_subplots(client_ids):
"""
For each client in client_ids, create a subplot in one figure:
- Left y-axis: active (blue=active, red=inactive) and trading days (green), with numeric ticks (0/1)
- Right y-axis: attrition probability over time
- Separate legends: left for 'Active', 'Inactive', 'Traded'; right for 'P(Inactive)'
- Title of each subplot shows the client ID
"""
n = len(client_ids)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=n, ncols=1, figsize=(12, 4*n), sharex=True)
if n == 1:
axes = [axes]
days = np.arange(T_test)
for ax1, cid in zip(axes, client_ids):
# gather P(inactive) values
p_vals = [
risk_df.loc[
(risk_df['client_id'] == cid) & (risk_df['time'] == t),
'p_inactive'
].item()
for t in days
]
# latent active flags and trading days
active_flag = active_df[T_train:][f'client_{cid}'].values
trade_days = Y_test.iloc[:, cid]
# Left axis: Active vs Inactive
idx_active = days[active_flag]
idx_inactive = days[~active_flag]
h_active = ax1.scatter(idx_active, [1]*len(idx_active), c='blue', marker='s', alpha=0.3, label='Active')
h_inactive = ax1.scatter(idx_inactive, [1]*len(idx_inactive), c='red', marker='s', alpha=0.3, label='Inactive')
# Left axis: actual trades (0 or 1)
h_trade = ax1.scatter(trade_days.index, trade_days.values,
c='green', marker='o', label='Traded')
# Set numeric ticks on left y-axis
ax1.set_ylim(-0.2, 1.2)
ax1.set_yticks([0, 1])
ax1.set_ylabel('Activity (0/1)')
ax1.set_title(f'Client {cid} Activity and Attrition Prob')
# Left-axis legend
ax1.legend(handles=[h_active, h_inactive, h_trade],
labels=['Active', 'Inactive', 'Traded'],
loc='upper left')
# Right axis: P(Inactive)
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
h_prob, = ax2.plot(days, p_vals, c='black', label='P(Inactive)')
ax2.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax2.set_ylabel('P(Inactive)')
# Right-axis legend
ax2.legend(handles=[h_prob], loc='upper right')
axes[-1].set_xlabel('Day')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Example: plot select clients in one figure
#plot_clients_subplots([3, 8, 9, 18])
plot_clients_subplots([3, 8, 9, 30])
Simulation of client abnormal behavior¶
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import poisson, norm
from collections import deque
def run_simulation(N_clients=50,
T=200,
reservation_price_mean=100,
reservation_price_std_pct=0.1,
lambda_mean=1,
lambda_std=0.05,
prior_mean=60,
prior_std=10,
reservation_price_noise_std=None,
discount_trigger_pct=0.35, # trigger threshold: 0.5 means 50% lower
boosted_rate_factor = 10,
hit_rate_target=0.4,
window_size=10,
attrition_threshold=0.1,
random_seed=42):
"""
Simulate RFQ interactions with Bayesian quantile pricing and client attrition.
Adds a mechanism: if a client gets a quote at least `discount_trigger_pct` below their reservation price,
they double their RFQ rate until the dealer quotes above their reservation price.
"""
np.random.seed(random_seed)
# Generate distribution of reservation prices
reservation_prices = np.random.normal(reservation_price_mean,
reservation_price_mean * reservation_price_std_pct,
N_clients)
# Noise in reservation prices
fair_price = reservation_price_mean
res_price_noise_std = reservation_price_noise_std or (fair_price * reservation_price_std_pct * 2)
res_price_noise_var = res_price_noise_std ** 2
# Base RfQ intensities
lambdas = np.abs(np.random.normal(lambda_mean, lambda_std, N_clients))
base_lambdas = lambdas.copy() # store for reset later
# Posterior beliefs
clients_posterior = {i: {'mean': prior_mean, 'var': prior_std ** 2,
'n': 0, 'sum_obs': 0.0}
for i in range(N_clients)}
z = norm.ppf(1 - hit_rate_target)
active = np.ones(N_clients, dtype=bool)
# Flags for tracking "boosted" mode
boosted = np.zeros(N_clients, dtype=bool)
# Track daily active/boosted status
active_flags = np.zeros((T, N_clients), dtype=bool)
boosted_flags = np.zeros((T, N_clients), dtype=bool)
daily_history = [deque(maxlen=window_size) for _ in range(N_clients)]
active_history = []
records = []
Y = np.zeros((T, N_clients), dtype=int) # binary: whether client sent at least one RFQ that day
for t in range(T):
daily_hits = np.zeros(N_clients, dtype=int)
daily_reqs = np.zeros(N_clients, dtype=int)
for i in range(N_clients):
if not active[i]:
continue
n_rfq = poisson.rvs(lambdas[i])
if n_rfq > 0:
Y[t, i] = 1
for _ in range(n_rfq):
post = clients_posterior[i]
price = max(0.0, post['mean'] + np.sqrt(post['var'] + res_price_noise_var) * z)
r = norm.rvs(reservation_prices[i], res_price_noise_std)
# Trading happens when price <= reservation price
hit = price <= r
daily_reqs[i] += 1
daily_hits[i] += int(hit)
# Check discount trigger
if price <= (1 - discount_trigger_pct) * r:
boosted[i] = True
lambdas[i] = base_lambdas[i] * boosted_rate_factor
elif boosted[i] and price > r / (1-discount_trigger_pct):
boosted[i] = False
lambdas[i] = base_lambdas[i]
# Update posterior belief
post['n'] += 1
post['sum_obs'] += r
post_var = 1 / (1 / (prior_std ** 2) + post['n'] / res_price_noise_var)
post['var'] = post_var
post['mean'] = post_var * (prior_mean / (prior_std ** 2) +
post['sum_obs'] / res_price_noise_var)
records.append({'time': t,
'client_id': i,
'price': price,
'reservation': r,
'hit': hit,
'boosted': boosted[i]})
# Update attrition status
for i in range(N_clients):
if not active[i] or daily_reqs[i] == 0:
continue
rate = daily_hits[i] / daily_reqs[i]
daily_history[i].append(rate)
if len(daily_history[i]) == window_size and np.mean(daily_history[i]) < attrition_threshold:
active[i] = False
active_history.append(int(active.sum()))
active_flags[t, :] = active.copy()
boosted_flags[t, :] = boosted.copy()
rfq_df = pd.DataFrame(records)
activity_df = pd.DataFrame(Y, columns=[f'client_{i}' for i in range(N_clients)])
active_df = pd.DataFrame(active_flags, columns=[f'client_{i}' for i in range(N_clients)])
boosted_df = pd.DataFrame(boosted_flags, columns=[f'client_{i}' for i in range(N_clients)])
return rfq_df, active_history, activity_df, active_df, boosted_df
# Run simulation
rfq_df, active_history, activity_df, active_df, boosted_df = run_simulation()
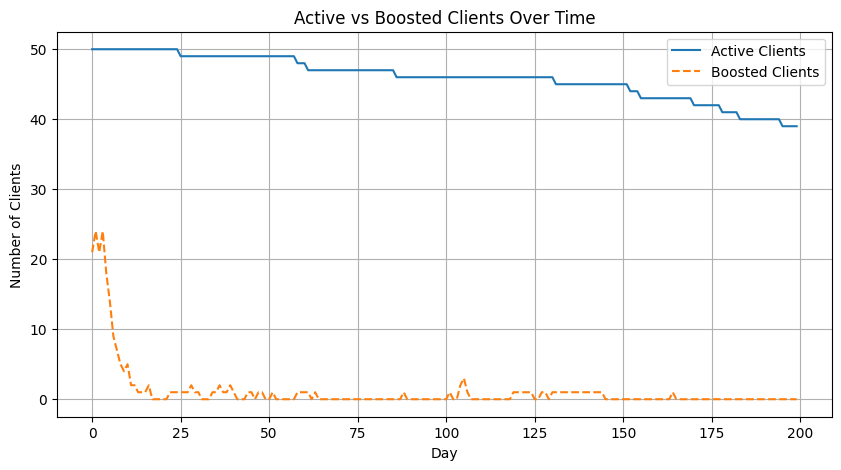
# Plot active and boosted clients over time
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.plot(active_df.sum(axis=1), label='Active Clients')
plt.plot(boosted_df.sum(axis=1), label='Boosted Clients', linestyle='--')
plt.xlabel('Day')
plt.ylabel('Number of Clients')
plt.title('Active vs Boosted Clients Over Time')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
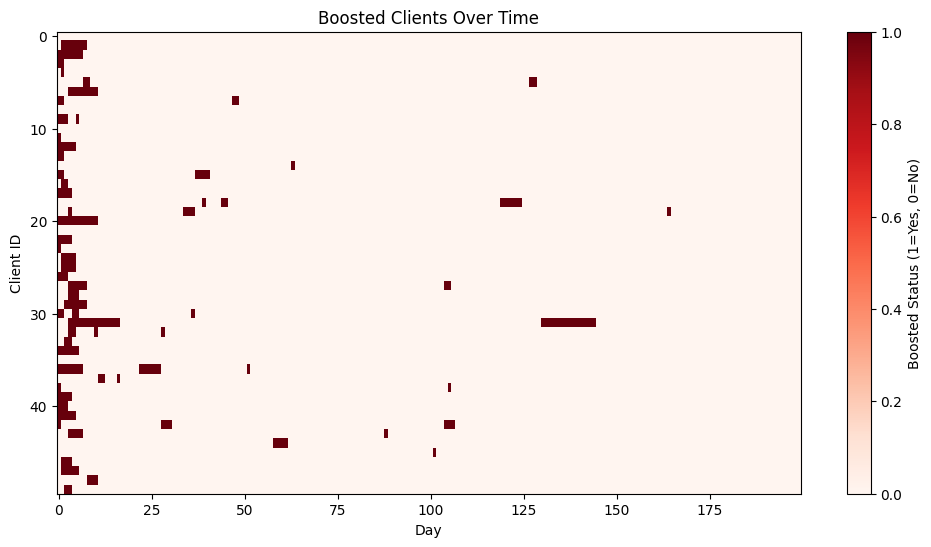
# Heatmap of boosted status
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
plt.imshow(boosted_df.T, aspect='auto', cmap='Reds')
plt.colorbar(label='Boosted Status (1=Yes, 0=No)')
plt.xlabel('Day')
plt.ylabel('Client ID')
plt.title('Boosted Clients Over Time')
plt.show()
from scipy.special import betaln, gammaln
from scipy.optimize import minimize
# -----------------------------
# Beta-Binomial mixture MLE with shared mean
# -----------------------------
def log_beta_binom_pmf(x, n, alpha, beta):
# log [ C(n,x) * B(alpha+x, beta+n-x) / B(alpha,beta) ]
return (
gammaln(n + 1) - gammaln(x + 1) - gammaln(n - x + 1)
+ betaln(alpha + x, beta + n - x)
- betaln(alpha, beta)
)
def neg_log_likelihood(params, xs, ns):
# params = [logit_mu, log_k_g, log_k_b, logit_qg]
logit_mu, log_k_g, log_k_b, logit_qg = params
mu = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-logit_mu)) # shared mean
k_g = np.exp(log_k_g) + 1e-8
k_b = np.exp(log_k_b) + 1e-8
qg = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-logit_qg))
# convert to alpha, beta
alpha_g, beta_g = mu * k_g, (1 - mu) * k_g
alpha_b, beta_b = mu * k_b, (1 - mu) * k_b
# mixture likelihood per client
ll = []
for x, n in zip(xs, ns):
log_p_g = log_beta_binom_pmf(x, n, alpha_g, beta_g)
log_p_b = log_beta_binom_pmf(x, n, alpha_b, beta_b)
# log-sum-exp for mixture
a = np.log(qg) + log_p_g
b = np.log(1 - qg) + log_p_b
m = max(a, b)
ll_i = m + np.log(np.exp(a - m) + np.exp(b - m))
ll.append(ll_i)
return -np.sum(ll)
def fit_beta_mixture_mle(activity_df, train_days):
"""
activity_df: (T x N) binary DataFrame
train_days: number of days used for training (first half)
Returns dict with fitted parameters.
"""
T, N = activity_df.shape
A = activity_df.iloc[:train_days].values # (train_days x N)
xs = A.sum(axis=0) # successes per client in training
ns = np.full_like(xs, fill_value=train_days)
# rough start for mean
p_hat = xs.mean() / train_days
logit_mu0 = np.log(p_hat / (1 - p_hat + 1e-8))
start = np.array([
logit_mu0,
np.log(10.0), # k_g initial concentration
np.log(2.0), # k_b initial concentration
0.0 # logit(0.5)
], dtype=float)
res = minimize(neg_log_likelihood, start, args=(xs, ns), method='L-BFGS-B')
logit_mu, log_k_g, log_k_b, logit_qg = res.x
mu = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-logit_mu))
k_g = np.exp(log_k_g) + 1e-8
k_b = np.exp(log_k_b) + 1e-8
params = {
'mu': float(mu),
'alpha_g': float(mu * k_g), 'beta_g': float((1 - mu) * k_g),
'alpha_b': float(mu * k_b), 'beta_b': float((1 - mu) * k_b),
'q_g': float(1 / (1 + np.exp(-logit_qg))),
'success': bool(res.success),
'message': res.message
}
return params
def posterior_good(x, n, params):
a_g = params['alpha_g']; b_g = params['beta_g']
a_b = params['alpha_b']; b_b = params['beta_b']
q_g = params['q_g']
log_p_g = log_beta_binom_pmf(x, n, a_g, b_g)
log_p_b = log_beta_binom_pmf(x, n, a_b, b_b)
a = np.log(q_g) + log_p_g
b = np.log(1 - q_g) + log_p_b
m = max(a, b)
num = np.exp(a - m)
den = num + np.exp(b - m)
return float(num / den)
# Fit on first half, removing first 25 days until it settles
T = activity_df.shape[0]
mid = T // 2
params = fit_beta_mixture_mle(activity_df[25:], train_days=mid)
# Detect abnormalities on second half using a sliding window
n_window = 10 # window size for detection, can be adjusted
threshold = 0.5 # classify as abnormal if p(good|D) < threshold
N = activity_df.shape[1]
abnormal_flags = np.zeros_like(activity_df.values, dtype=bool)
# For each day t in the second half, use the last n_window days (bounded within the second half)
for t in range(mid, T):
start = max(mid, t - n_window + 1)
end = t + 1
window = activity_df.iloc[start:end].values # (w x N)
n = window.shape[0]
x = window.sum(axis=0)
# Posterior for each client
p_good = np.array([posterior_good(int(xi), int(n), params) for xi in x])
abnormal_flags[t, :] = p_good < threshold
abnormal_df = pd.DataFrame(abnormal_flags, columns=activity_df.columns, index=activity_df.index)
params{'mu': 0.6459024041525655,
'alpha_g': 17819.14219878137,
'beta_g': 9768.837168102045,
'alpha_b': 0.6772910514791353,
'beta_b': 0.3713055277018204,
'q_g': 0.892871535754001,
'success': True,
'message': 'CONVERGENCE: REL_REDUCTION_OF_F_<=_FACTR*EPSMCH'}import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.stats import beta
def plot_fitted_betas(params, bins=200):
"""
Plot fitted good vs bad Beta distributions.
params: dict returned by fit_beta_mixture_mle
"""
a_g, b_g = params['alpha_g'], params['beta_g']
a_b, b_b = params['alpha_b'], params['beta_b']
q_g = params['q_g']
# Grid
x = np.linspace(0, 1, bins)
# Densities
pdf_g = beta.pdf(x, a_g, b_g)
pdf_b = beta.pdf(x, a_b, b_b)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(x, pdf_g, label=f"Good (α={a_g:.2f}, β={b_g:.2f})", lw=2, color="blue")
plt.plot(x, pdf_b, label=f"Bad (α={a_b:.2f}, β={b_b:.2f})", lw=2, color="red")
plt.fill_between(x, pdf_g, alpha=0.2, color="blue")
plt.fill_between(x, pdf_b, alpha=0.2, color="red")
plt.title("Fitted Beta Distributions (Good vs Bad)")
plt.xlabel("Success probability")
plt.ylabel("Density")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, ls="--", alpha=0.5)
plt.show()
plot_fitted_betas(params)
# Use a previous window (exclude day t) when computing P(good|D)
n_window = 10
threshold = 0.5
def build_pgood_panel(activity_df, boosted_df, active_df, params, mid, n_window, threshold):
T, N = activity_df.shape
rows = []
# Start at mid + n_window to ensure a full *previous* window exists
for t in range(mid + n_window, T):
start = t - n_window
end = t # exclude day t
window = activity_df.iloc[start:end] # (n_window x N)
x = window.sum(axis=0).values.astype(int) # successes per client in previous window
n = n_window
# compute p_good for each client
p_goods = []
for j in range(N):
p = posterior_good(int(x[j]), int(n), params)
p_goods.append(p)
p_goods = np.array(p_goods)
# flags at time t
boosted_t = boosted_df.iloc[t].values.astype(bool)
active_t = active_df.iloc[t].values.astype(bool)
inactive_t = ~active_t
traded_today = activity_df.iloc[t].values.astype(int)
for j in range(N):
rows.append({
'day': t,
'client_id': j,
'x': int(x[j]),
'n': int(n),
'p_good': float(p_goods[j]),
'abnormal': bool(p_goods[j] < threshold),
'boosted': bool(boosted_t[j]),
'inactive': bool(inactive_t[j]),
'traded_today': int(traded_today[j])
})
panel = pd.DataFrame(rows)
return panel
panel_df = build_pgood_panel(activity_df, boosted_df, active_df, params, mid, n_window, threshold)
# Correctly aligned daily summary for second half *with windowing*
days = sorted(panel_df['day'].unique())
daily_summary = panel_df.groupby('day').agg(
abnormal_count=('abnormal', 'sum'),
boosted_count=('boosted', 'sum'),
inactive_count=('inactive', 'sum')
).reset_index()
# Overlap summary on client-day panel
overlap_summary = {
'days_evaluated': int(len(days)),
'clients': int(N),
'total_client_days': int(panel_df.shape[0]),
'abnormal_client_days': int(panel_df['abnormal'].sum()),
'boosted_client_days': int(panel_df['boosted'].sum()),
'inactive_client_days': int(panel_df['inactive'].sum()),
'abnormal_and_boosted': int((panel_df['abnormal'] & panel_df['boosted']).sum()),
'abnormal_and_inactive': int((panel_df['abnormal'] & panel_df['inactive']).sum()),
'abnormal_not_boosted_or_inactive': int((panel_df['abnormal'] & ~panel_df['boosted'] & ~panel_df['inactive']).sum())
}
overlap_df2 = pd.DataFrame([overlap_summary])
# Heatmap of p_good by client (days x clients) for visual inspection
# Build a matrix with rows=days, cols=clients
days_idx = daily_summary['day'].values
pgood_mat = np.full((len(days_idx), N), np.nan)
for i, t in enumerate(days_idx):
slice_t = panel_df[panel_df['day'] == t].sort_values('client_id')
pgood_mat[i, :] = slice_t['p_good'].values
plt.figure(figsize=(12,6))
plt.imshow(pgood_mat.T, aspect='auto')
plt.colorbar(label='P(good | previous window)')
plt.xlabel('Day index in second half')
plt.ylabel('Client ID')
plt.title('Per-client P(good|D) over time (previous window)')
plt.show()

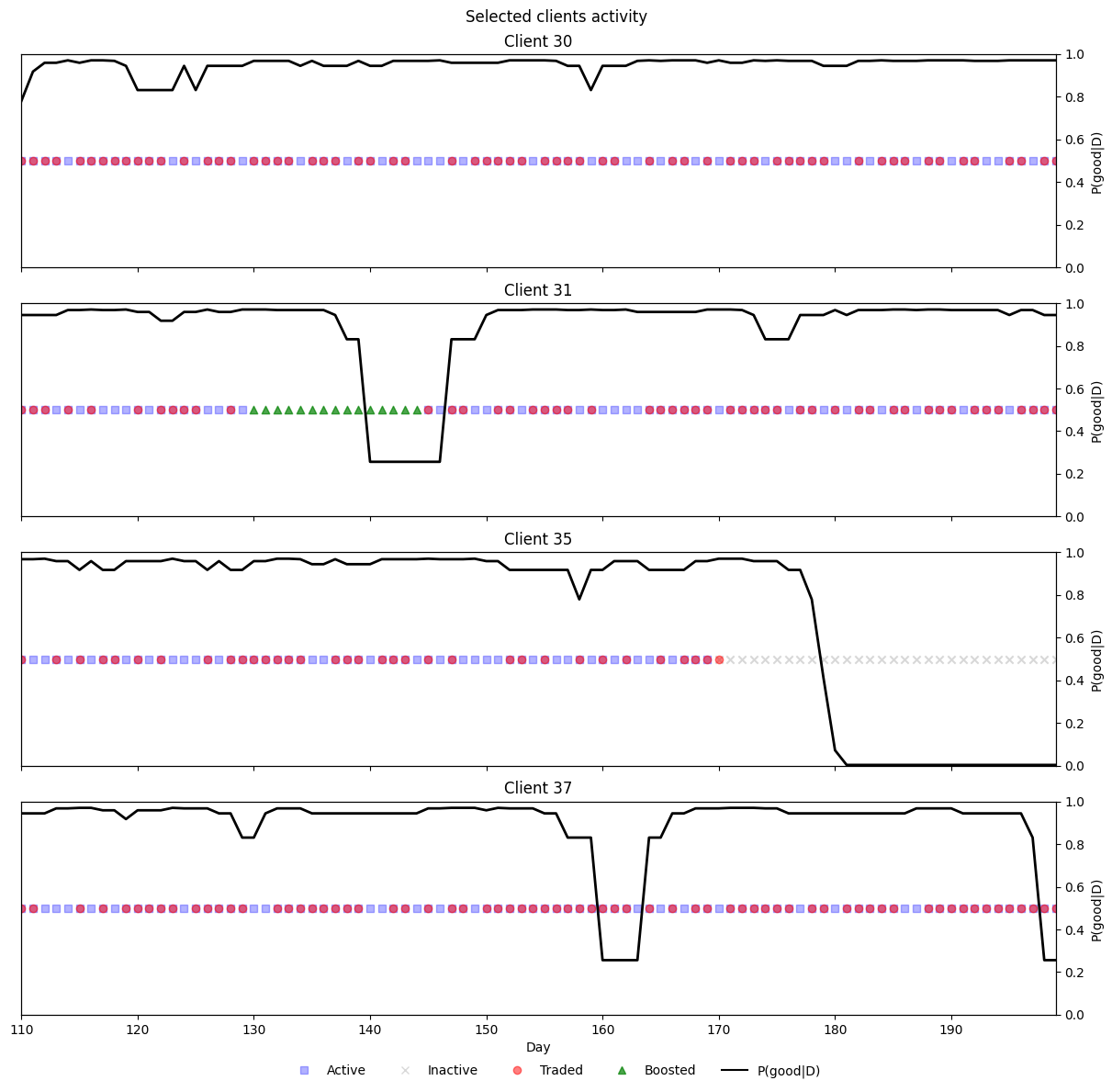
from matplotlib.lines import Line2D
def plot_clients_activity_prob(clients, df):
"""
One figure with one row per client.
On boosted days, only the 'Boosted' marker is shown (others hidden).
"""
clients = list(clients)
n = len(clients)
if n == 0:
return
fig, axes = plt.subplots(n, 1, figsize=(12, 2.8 * n), sharex=True, constrained_layout=True)
if n == 1:
axes = [axes]
# Build a single, global legend
legend_elems = [
Line2D([0],[0], marker='s', linestyle='None', color='blue', alpha=0.3, label='Active'),
Line2D([0],[0], marker='x', linestyle='None', color='gray', alpha=0.3, label='Inactive'),
Line2D([0],[0], marker='o', linestyle='None', color='red', alpha=0.5, label='Traded'),
Line2D([0],[0], marker='^', linestyle='None', color='green', alpha=0.7, label='Boosted'),
Line2D([0],[0], linestyle='-', color='black', label='P(good|D)'),
]
x_min, x_max = None, None
for ax, cid in zip(axes, clients):
df_c = df[df['client_id'] == cid].sort_values('day').copy()
if df_c.empty:
ax.set_title(f"Client {cid} (no data)")
ax.set_yticks([])
continue
# Masks
boosted_mask = df_c['boosted']
active_mask = (~df_c['inactive']) & (~boosted_mask)
inactive_mask = df_c['inactive'] & (~boosted_mask)
traded_mask = (df_c['traded_today'] == 1) & (~boosted_mask)
# Scatter statuses
ax.scatter(df_c['day'][active_mask], [1]*active_mask.sum(), c='blue', marker='s', alpha=0.3)
ax.scatter(df_c['day'][inactive_mask], [1]*inactive_mask.sum(), c='gray', marker='x', alpha=0.3)
ax.scatter(df_c['day'][traded_mask], [1]*traded_mask.sum(), c='red', marker='o', alpha=0.5)
ax.scatter(df_c['day'][boosted_mask], [1]*boosted_mask.sum(), c='green', marker='^', alpha=0.7, zorder=3)
ax.set_yticks([])
ax.set_ylim(0.5, 1.5)
# p_good
ax2 = ax.twinx()
ax2.plot(df_c['day'], df_c['p_good'], color='black', lw=2)
ax2.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax2.set_ylabel("P(good|D)")
ax.set_title(f"Client {cid}")
# Track x-lims
dmin, dmax = df_c['day'].min(), df_c['day'].max()
x_min = dmin if x_min is None else min(x_min, dmin)
x_max = dmax if x_max is None else max(x_max, dmax)
axes[-1].set_xlabel("Day")
if x_min is not None and x_max is not None:
axes[-1].set_xlim(x_min, x_max)
fig.suptitle("Selected clients activity", y=1.02)
# Move legend below figure
fig.legend(handles=legend_elems, loc='lower center', ncol=5, frameon=False, bbox_to_anchor=(0.5, -0.03))
plt.show()
plot_clients_activity_prob([30,31,35, 37], panel_df)
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
def _cm_df(cm, labels=("Pred 0", "Pred 1"), index=("True 0", "True 1")):
"""Pretty dataframe for a 2x2 confusion matrix."""
return pd.DataFrame(cm, index=index, columns=labels)
def evaluate_confusions(panel_df, normalize=False):
"""
Evaluate confusion matrices without recomputing thresholds.
Uses:
- df['abnormal'] as the model's predicted abnormal label (already thresholded).
- df['inactive'] and df['boosted'] as operational labels.
- Global abnormality = (inactive OR boosted).
Returns dict with both raw arrays and pretty DataFrames.
Set normalize=True to return per-true-class rates instead of counts.
"""
df = panel_df.copy()
# Ensure ints
y_abnormal = df["abnormal"].astype(int).values
y_inactive = df["inactive"].astype(int).values
y_boosted = df["boosted"].astype(int).values
# Global abnormality (prediction-side for the overall CM)
y_global_abn = (df["inactive"] | df["boosted"]).astype(int).values
# Normalization mode for sklearn
norm_mode = "true" if normalize else None
results = {}
# 1) Inactive (truth) vs Abnormal (model)
cm_inactive = confusion_matrix(y_inactive, y_abnormal, labels=[0,1], normalize=norm_mode)
results["inactive_vs_abnormal"] = cm_inactive
results["inactive_vs_abnormal_df"] = _cm_df(cm_inactive)
# 2) Boosted (truth) vs Abnormal (model)
cm_boosted = confusion_matrix(y_boosted, y_abnormal, labels=[0,1], normalize=norm_mode)
results["boosted_vs_abnormal"] = cm_boosted
results["boosted_vs_abnormal_df"] = _cm_df(cm_boosted)
# 3) OVERALL: Abnormal (truth) vs Global abnormality (prediction = inactive OR boosted)
cm_overall = confusion_matrix(y_abnormal, y_global_abn, labels=[0,1], normalize=norm_mode)
results["overall_abnormal_vs_global"] = cm_overall
results["overall_abnormal_vs_global_df"] = _cm_df(cm_overall)
return results
# Example usage:
cm_results = evaluate_confusions(panel_df, normalize=False)
print("Inactive (truth) vs Abnormal (model):\n", cm_results["inactive_vs_abnormal_df"], "\n")
print("Boosted (truth) vs Abnormal (model):\n", cm_results["boosted_vs_abnormal_df"], "\n")
print("Overall: Abnormal (truth) vs Global (inactive OR boosted) prediction:\n", cm_results["overall_abnormal_vs_global_df"])
Inactive (truth) vs Abnormal (model):
Pred 0 Pred 1
True 0 3830 74
True 1 56 540
Boosted (truth) vs Abnormal (model):
Pred 0 Pred 1
True 0 3867 609
True 1 19 5
Overall: Abnormal (truth) vs Global (inactive OR boosted) prediction:
Pred 0 Pred 1
True 0 3811 75
True 1 69 545